There is considerable controversy over the total number of genes in the human genome. The number of protein-coding genes is pretty well established at somewhere between 19,500 and 20,000. It's the number of non-coding genes that's disputed.
There's general agreement on the number of well-defined small RNA genes such as snRNAs, snoRNA, microRNAs etc. Similarly, the number of ribosomal RNA and tRNA genes is known. The problem is with identifying genuine long non-coding RNA genes (lncRNA genes). Estimates vary from less than 20,000 to more than 200,000 but most of these estimates fail to define what they mean by "gene." Many scientists seem to think that any detectable transcript must come from a gene.
This doesn't make any sense since we know that spurious transcripts exist and they don't come from genes by any meaningful definition of gene. The only reasonable definition of a molecular gene is a DNA sequence that's transcribed to produce a functional product.1
The idea that spurious, non-functional, transcripts exist has been described in the scientific literature for many decades. One of my favorites is in a paper by Ponting and Haerty (2022) quoting another paper from thirteen years ago by Ulitsky and Bartel.
The cellular transcriptional machinery does not perfectly discriminate cryptic promoters from functional gene promoters. This machinery is abundant and so can engage sites momentarily depleted of nucleosomes and rapidly initiate transcription. The chance occurrence of splice sites can then facilitate the capping, splicing, and polyadenylation of long transcripts. A very large number of such rare RNA species are detectable in RNA-sequencing experiments whose properties are virtually indistinguishable from those of bona fide lncRNAs. Consequently, “a sensible [null] hypothesis is that most of the currently annotated long (typically >200 nt) noncoding RNAs are not functional, i.e., most impart no fitness advantage, however slight” (Ulitsky and Bartel, 2013: p. 26).
The important point here is that the correct null hypothesis is that these transcripts don't have a biologically relevant function and the burden of proof is on researchers to demonstrate function before assigning them to a genuine gene. My colleagues at the University of Toronto made the same point in a paper published in 2015.
In the absence of sufficient evidence, a given ncRNA should be provisionally labeled as non-functional. Subsequently, if the ncRNA displays features/activities beyond what one would expect for the null hypothesis, then we can reclassify the ncRNA in question as being functional. (Palazzo and Lee, 2015)
There are a number of well-defined lncRNAs that have been shown to have distinct reproducible functions. The key question is how many of these biologically relevant lncRNA genes exist in the human genome. I struggled with the answer to this question when I was writing my book. I finally decided to make a generous estimate of 5000 non-coding genes and that implies several thousand lncRNA genes (p. 127). I now think that estimate was far too generous and there are probably fewer than 1000 genuine lncRNA genes.
I have not scoured the literature for all the examples of human lncRNAs having good evidence of function but my impression is that there are only a few hundred. This post was incited by a recent publication by researchers from the Hospital for Sick Children and the University of Toronto (Toronto, Canada) who characterized another functional lncRNA called CISTR-ACT that plays a role in regulating cell size (Kiriakopulos et al., 2025).
I was prompted to revisit this controversy by the accompanying press release that said ...
Unlike genes that encode for proteins, CISTR-ACT is a long non-coding RNA (or lncRNA) and is part of the non-coding genome, the largely unexplored part that makes up 98 per cent of our DNA. This research helps show that the non-coding genome, often dismissed as ‘junk DNA’, plays an important role in how cells function.
We're used to this kind of misinformation2 in press releases but I thought it would be a good idea to read the paper. As I expected, there's nothing in the paper about junk DNA but here's the first sentence of the introduction.
The human genome contains more long non-coding RNAs (lncRNAs) than protein-coding genes (GENCODE v49) which regulate genes and chromatin scaffolding.
The latest version of GENCODE Release 49 claims that there are 35,899 lncRNA genes. This is the only reference in the Kiriakopulos et al. paper to the number of lncRNA genes. There's no mention of the controversy and none of the papers that discuss the controversy are referenced.
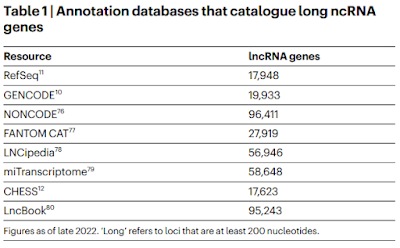
The GENCODE number is close to the latest version of Ensembl, which lists 35,042 lncRNA genes. I couldn't find any good explanation for these numbers or for the definition of "gene" that they are using but what's interesting is how these numbers are climbing every year; for example, a paper from two years ago listed a number of sources and you can see that the RefSeq and GENCODE numbers are much smaller than today's numbers (Amaral et al., 2023).3
We intend to provoke alternative interpretation of questionable evidence and thorough inquiry into unsubstantiated claims.
Ponting and Haerty (2022)
It's perfectly acceptable to state your preferred view on lncRNAs when you publish a paper. The authors of the recent paper may want to believe that there are more lncRNA genes than protein-coding genes but I think it's important for them to define what they mean by "gene" when they make such a claim. What's not acceptable, in my opinion, is to ignore a genuine scientific controversy by not mentioning in the introduction that there are other legitimate views.
It's a shame that they didn't do that because their paper is a good example of the hard work that needs to be done in order to demonstrate that a particular lncRNA has a biologically relevant function.
In closing, I want to emphasize the recent review by Ponting and Haerty (2022)4 that points out the importance of the problem and the kinds of experiments that need to be done in order to establish that a given RNA comes from a real gene. This is how a scientific controversy should be addressed. Here's the abstract of that paper ...
Do long noncoding RNAs (lncRNAs) contribute little or substantively to human biology? To address how lncRNA loci and their transcripts, structures, interactions, and functions contribute to human traits and disease, we adopt a genome-wide perspective. We intend to provoke alternative interpretation of questionable evidence and thorough inquiry into unsubstantiated claims. We discuss pitfalls of lncRNA experimental and computational methods as well as opposing interpretations of their results. The majority of evidence, we argue, indicates that most lncRNA transcript models reflect transcriptional noise or provide minor regulatory roles, leaving relatively few human lncRNAs that contribute centrally to human development, physiology, or behavior. These important few tend to be spliced and better conserved but lack a simple syntax relating sequence to structure and mechanism, and so resist simple categorization. This genome-wide view should help investigators prioritize individual lncRNAs based on their likely contribution to human biology.
1. See Wikipedia: Gene; What Is a Gene?; Definition of a gene (again); Must a Gene Have a Function?.
2. No knowledgeable scientist ever said that all non-coding DNA was junk. We've known about non-coding genes for more than half-a-century.
3. See How many genes in the human genome (2023)?
4. See Most lncRNAs are junk
Amaral, P., Carbonell-Sala, S., De La Vega, F.M., Faial, T., Frankish, A., Gingeras, T., Guigo, R., Harrow, J.L., Hatzigeorgiou, A.G., Johnson, R. et al. (2023) The status of the human gene catalogue. Nature 622:41-47. [doi: 10.1038/s41586-023-06490-x]
Kiriakopulos et al. (2025) LncRNA CISTR-ACT regulates cell size in human and mouse by guiding FOSL2. Nature communications: (in press). [doi: 10.1038/s41467-025-67591-x]
Palazzo, A.F. and Lee, E.S. (2015) Non-coding RNA: what is functional and what is junk? Frontiers in genetics 6:2(1-11). [doi: 10.3389/fgene.2015.00002]
Ponting, C.P. and Haerty, W. (2022) Genome-Wide Analysis of Human Long Noncoding RNAs: A Provocative Review. Annual review of genomics and human genetics 23. [doi: 10.1146/annurev-genom-112921-123710
Ulitsky, I. and Bartel, D.P. (2013) lincRNAs: genomics, evolution, and mechanisms. Cell 154:26-46. [doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2013.06.020]