The Nobel Prize in Chemistry 2008.
"for the discovery and development of the green fluorescent protein, GFP"
 Roger Y. Tsien (1952 - ) won the Nobel Prize in Chemistry for his work on adapting green fluorescent protein to serve as a marker for detecting changes within a cell. He shared the prize with Osamu Shimomura and Martin Chalfie.
Roger Y. Tsien (1952 - ) won the Nobel Prize in Chemistry for his work on adapting green fluorescent protein to serve as a marker for detecting changes within a cell. He shared the prize with Osamu Shimomura and Martin Chalfie.Tsien's lab learned what causes the protein to flouresce and how to modify the active site on order to create variants that emitted different colors. You can watch an excellent video of his Nobel Lecture: Constructing and Exploiting the Fluorescent Protein Paintbox.
If that's a little too technical, the work is described in a special document called Information for the Public.
THEME:
Nobel Laureates
This is where the third Nobel Prize laureate Roger Tsien makes his entry. His greatest contribution to the GFP revolution was that he extended the researchers’ palette with many new colours that glowed longer and with higher intensity.
To begin with, Tsien charted how the GFP chromophore is formed chemically in the 238-aminoacid-long GFP protein. Researchers had previously shown that three amino acids in position 65–67 react chemically with each other to form the chromosphore. Tsien showed that this chemical reaction requires oxygen and explained how it can happen without the help of other proteins.
With the aid of DNA technology, Tsien took the next step and exchanged various amino acids in different parts of GFP. This led to the protein both absorbing and emitting light in other parts of the spectrum. By experimenting with the amino acid composition, Tsien was able to develop new variants of GFP that shine more strongly and in quite different colours such as cyan, blue and yellow. That is how researchers today can mark different proteins in different colours to see their interactions.
One colour, however, that Tsien could not produce with GFP was red. Red light penetrates biological tissue more easily and is therefore especially useful for researchers who want to study cells and organs inside the body.
At this point, Mikhail Matz and Sergei Lukyanov, two Russian researchers, became involved in the GFP revolution. They looked for GFP-like proteins in fluorescent corals and found six more proteins, one red, one blue and the rest green.
The desired red protein, DsRED, was unfortunately larger and heavier than GFP. DsRED consisted of four amino acid chains instead of one and was of less use as a fluorescent tag in biological processes. Tsien’s research group solved this problem, redesigning DsRED so that the protein is now stable and fluoresces as a single amino acid chain, which can easily be connected to other proteins.From this smaller protein, Tsien’s research group also developed proteins with mouth watering names like mPlum, mCherry, mStrawberry, mOrange and mCitrine, according to the colour they glowed. Several other researchers and companies have also contributed new colours to this growing palette. So today, 46 years after Shimomura first wrote about the green fluorescent protein, there is a kaleidoscope of GFP-like proteins which shine with all the colours of the rainbow.
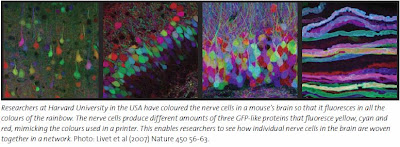
The brainbow
Three of these proteins have been used by researchers in a spectacular experiment. Mice were genetically modified to produce varying amounts of the colours yellow, cyan and red within the nerve cells of their brain. This combination of colours is similar to the one used by computer printers. The result was a mouse brain that glowed in the colours of the rainbow. The researchers could follow nerve fibres from individual cells in the dense network in the brain.
The researchers called this experiment “the brainbow”.
[Photo Credit: UCSD]
The images of the Nobel Prize medals are registered trademarks of the Nobel Foundation (© The Nobel Foundation). They are used here, with permission, for educational purposes only.